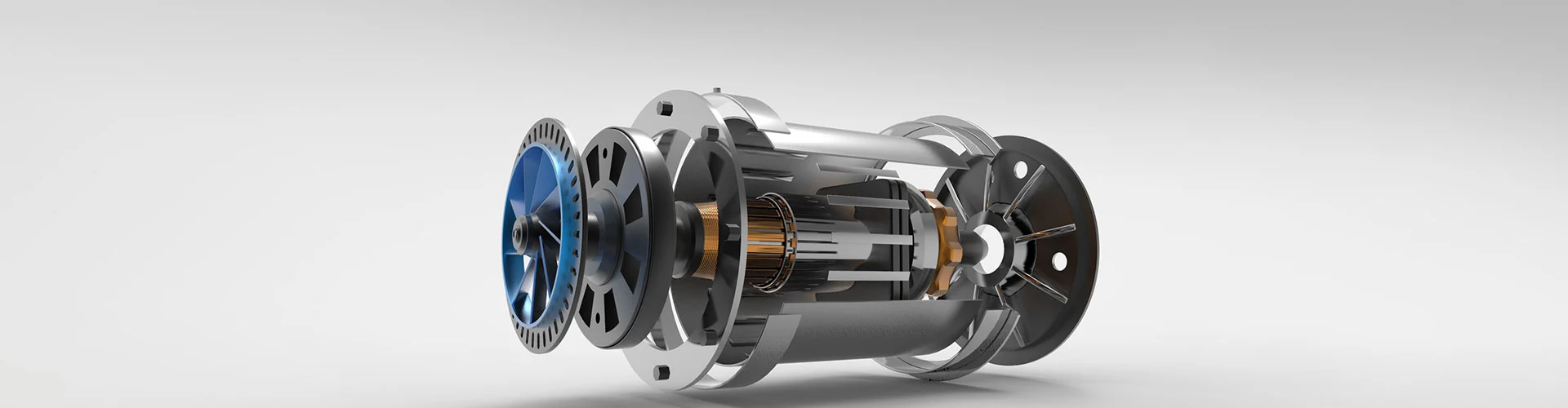
A synchronous motor is an AC motor in which the rotation of the shaft is synchronized with the frequency of the supply current. It operates at a constant speed, regardless of the load, as long as the load does not exceed the motor's maximum capacity. These motors are widely used in applications requiring precise speed control and high efficiency, such as industrial machinery, robotics, and power generation systems.
Key Features and Advantages
- Constant Speed Operation: Maintains a fixed speed under varying load conditions, ensuring consistent performance.
- High Efficiency: Achieves efficiency levels up to 95%, reducing energy consumption and operational costs.
- Power Factor Correction: Can be used to improve the power factor of electrical systems, enhancing overall efficiency.
- Durability: Constructed with robust materials for long service life in demanding environments.
- Low Maintenance: Requires minimal upkeep due to simple design and reliable components.
Product Specifications
Our synchronous motors are designed to meet high industrial standards. Below are the detailed parameters for our standard models.
Standard Model Parameters
| Model |
Power Rating (kW) |
Voltage (V) |
Frequency (Hz) |
Speed (RPM) |
Efficiency (%) |
Frame Size |
| SM-100 |
1.5 |
230/460 |
50/60 |
1500/1800 |
92 |
56 |
| SM-200 |
3.7 |
400 |
50 |
1500 |
93 |
80 |
| SM-300 |
7.5 |
460 |
60 |
1800 |
94 |
112 |
| SM-400 |
15 |
575 |
60 |
1200 |
95 |
160 |
| SM-500 |
22 |
690 |
50 |
1000 |
95 |
180 |
Environmental and Operational Specifications
| Parameter |
Value |
| Insulation Class |
F |
| Protection Class |
IP55 |
| Ambient Temperature |
-20°C to +40°C |
| Cooling Method |
IC 411 (Fan Cooled) |
| Mounting |
Foot Mounted (B3) |
Applications of Synchronous Motors
- Industrial Drives: Used in conveyor systems, compressors, and pumps where constant speed is critical.
- Power Generation: Employed as generators in power plants due to their ability to maintain grid frequency.
- Robotics: Ideal for precise motion control in automated systems.
- HVAC Systems: Used in large commercial heating, ventilation, and air conditioning units for efficient operation.
- Textile Machinery: Provides consistent speed for spinning and weaving processes.
Synchronous Motor FAQ
Q: What is the main difference between a synchronous motor and an induction motor?
A: The key difference is that a synchronous motor runs at a speed synchronized with the supply frequency, while an induction motor runs slightly slower than the synchronous speed due to slip. Synchronous motors are more efficient and offer better power factor control, but they require an external DC excitation source for operation.
Q: How do I select the right synchronous motor for my application?
A: Consider factors such as power requirements, voltage supply, operating speed, load characteristics, and environmental conditions. Our standard models cover a wide range, but custom options are available for specific needs. Consulting with our technical team can help ensure the best fit.
Q: Can synchronous motors be used for variable speed applications?
A: Traditionally, synchronous motors are constant speed devices. However, with modern variable frequency drives (VFDs), they can operate at variable speeds while maintaining synchronization. This allows for flexible control in applications like pumps and fans.
Q: What maintenance is required for a synchronous motor?
A: Maintenance is minimal and includes regular inspections of bearings, brushes (if equipped), and cooling systems. Lubrication may be needed periodically based on usage. Ensure the motor is kept clean and free from dust to prevent overheating.
Q: Are synchronous motors suitable for high-temperature environments?
A: Yes, our motors are designed with insulation class F, allowing them to operate efficiently in ambient temperatures up to 40°C. For higher temperatures, special designs or cooling methods can be implemented.
Q: How does a synchronous motor help in power factor correction?
A: Synchronous motors can be operated at a leading power factor by adjusting the field excitation. This capability allows them to compensate for lagging power factors in industrial plants, improving overall system efficiency and reducing utility penalties.
Q: What is the typical lifespan of a synchronous motor?
A: With proper maintenance and operating within specified parameters, our synchronous motors can last 20 years or more. Factors such as load conditions, environment, and maintenance practices influence longevity.
Q: Do you offer custom synchronous motor solutions?
A: Yes, we provide custom-designed motors tailored to specific requirements, including unusual voltages, speeds, mounting options, and environmental adaptations. Contact our engineering team for detailed discussions.