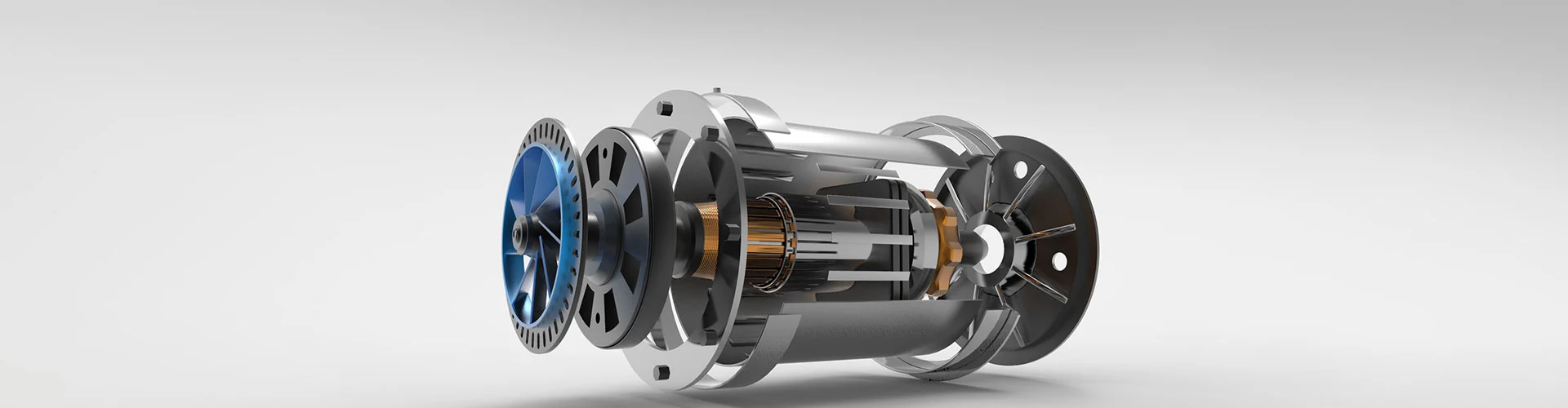
What is a Brake Motor?
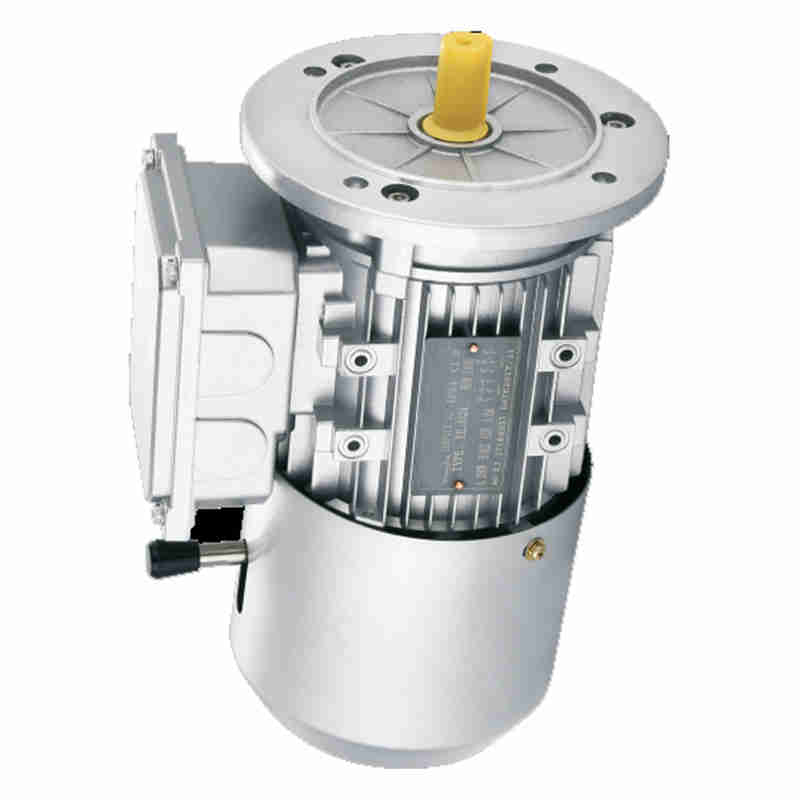
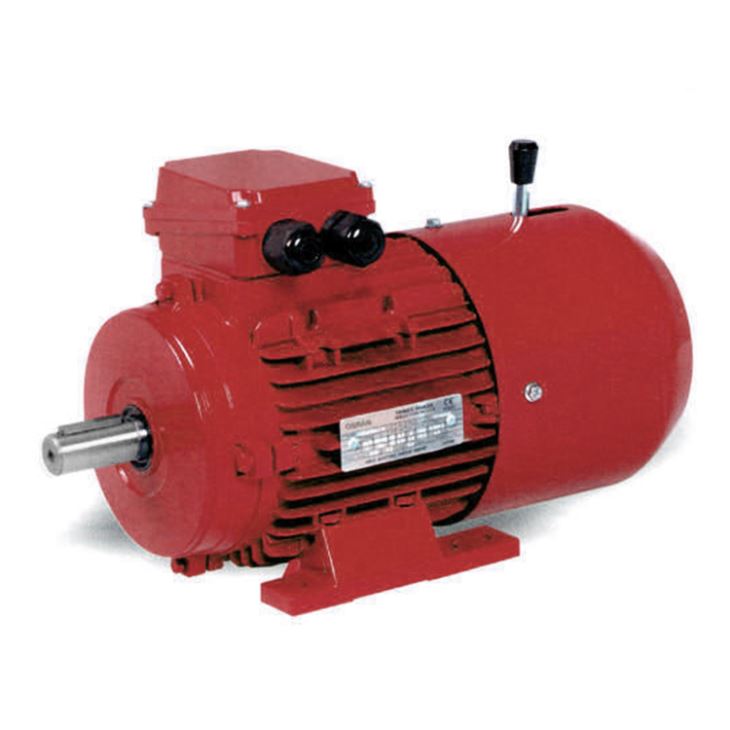
A brake motor is an integrated electromechanical device combining an electric motor with an automatic brake system. Designed for applications requiring rapid stopping, holding loads, or preventing unintended movement, brake motors are essential in industries such as material handling, automation, and industrial machinery. The brake engages automatically when power is cut off, providing safety and precision in operations.
Key Features of Brake Motors
- Instant braking action upon power loss
- High torque output for reliable holding
- Thermal protection to prevent overheating
- Compact design for easy integration
- Low maintenance and durable construction
- Compatible with various voltage inputs
Technical Specifications
Our brake motors are engineered to meet rigorous industrial standards. Below is a detailed table of specifications for our standard models.
| Model |
Power (kW) |
Voltage (V) |
Speed (RPM) |
Brake Torque (Nm) |
Insulation Class |
Weight (kg) |
| BM-100 |
0.75 |
230/400 |
1400 |
15 |
F |
18 |
| BM-200 |
1.5 |
230/400 |
1400 |
30 |
F |
25 |
| BM-300 |
2.2 |
400 |
2800 |
50 |
H |
32 |
| BM-400 |
4.0 |
400 |
1400 |
80 |
H |
45 |
| BM-500 |
7.5 |
400 |
2800 |
120 |
H |
60 |
Applications of Brake Motors
Brake motors are versatile and used in numerous industries for safety and control. Common applications include:
- Elevators and hoists for precise stopping
- Conveyor systems to prevent rollback
- CNC machines for accurate positioning
- Automated doors and gates
- Medical equipment requiring secure holds
- Packaging machinery for synchronized operations
Advantages of Using Our Brake Motors
- Enhanced safety with fail-safe braking
- Energy efficiency through optimized design
- Reduced downtime with robust components
- Easy installation and compatibility
- Compliance with international standards (e.g., IEC, NEMA)
Brake Motor FAQ
How does a brake motor work?
A brake motor operates by using an electromagnetic brake that engages when the motor is de-energized. The brake spring applies pressure to the brake disc, creating friction that stops the motor shaft. When power is applied, the electromagnetic field releases the brake, allowing the motor to run freely.
What is the difference between a brake motor and a standard motor?
A brake motor includes an integrated braking mechanism that activates upon power loss, whereas a standard motor lacks this feature and may require external braking systems. This makes brake motors ideal for applications where stopping precision and safety are critical.
Can brake motors be used in hazardous environments?
Yes, certain models are designed with explosion-proof enclosures and certifications for use in hazardous areas. Always check the specifications for ratings such as ATEX or IECEx to ensure suitability for specific environments.
How often should the brake be maintained?
Maintenance intervals depend on usage intensity and operating conditions. Generally, inspect the brake lining and components every 6 to 12 months for wear. Regular checks ensure optimal performance and longevity.
What causes brake noise and how can it be reduced?
Brake noise often results from dust accumulation, misalignment, or worn brake pads. To reduce noise, keep the brake clean, ensure proper alignment during installation, and replace worn components promptly. Using high-quality brake materials also minimizes noise.
Are brake motors reversible?
Yes, most brake motors are reversible and can operate in both directions. The braking function works independently of rotation direction, engaging whenever power is cut off.
What voltages are available for brake motors?
Brake motors are available in various voltage configurations, including 115V, 230V, 400V, and 460V, to match regional power standards. Always verify the voltage requirements based on your location and application.
How do I select the right brake motor for my application?
Consider factors such as required torque, power rating, speed, duty cycle, and environmental conditions. Refer to the technical specifications table and consult with our engineering team for tailored recommendations based on your needs.
Installation and Wiring Guidelines
Proper installation ensures optimal performance and safety. Follow these steps:
- Mount the motor securely on a flat, stable surface using appropriate bolts.
- Connect the power supply wires according to the wiring diagram provided, ensuring correct voltage and phase matching.
- For the brake circuit, connect the brake leads to the designated terminals, often labeled BR1 and BR2.
- Verify all connections are tight and insulated to prevent short circuits.
- Test the motor without load first to check rotation direction and brake engagement.
- Perform a loaded test to ensure the brake holds adequately under operational conditions.
Always adhere to local electrical codes and safety regulations during installation.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
- Regularly clean the motor and brake assembly to remove dust and debris.
- Check brake lining thickness every 6 months; replace if worn beyond specified limits.
- Lubricate bearings as per manufacturer guidelines to reduce friction and wear.
- Monitor operating temperature; overheating may indicate issues requiring attention.
- Inspect electrical connections periodically for corrosion or looseness.