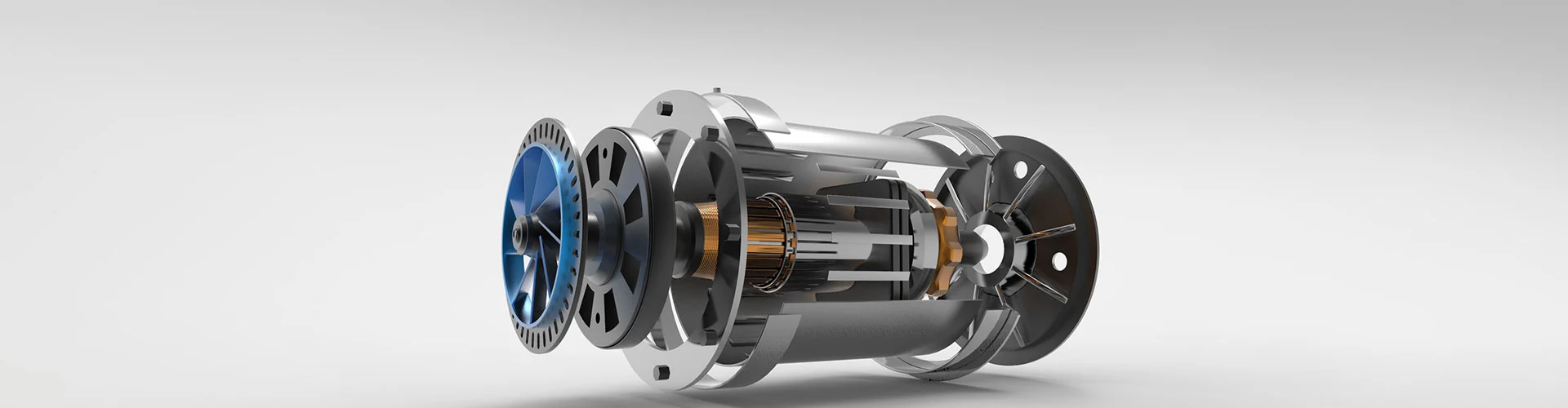
Introduction to Stepper Motors
A stepper motor is a brushless, synchronous electric motor that converts digital pulses into mechanical shaft rotation. Its movement is divided into discrete steps, allowing for precise control of position, speed, and acceleration without the need for feedback systems in many applications. Stepper motors are widely used in industries such as robotics, CNC machinery, 3D printing, medical devices, and automation systems due to their reliability, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness.
Key Features of Our Stepper Motors
- High torque output with minimal vibration
- Excellent positioning accuracy and repeatability
- Open-loop control compatibility, reducing system complexity
- Durable construction with long operational lifespan
- Low maintenance requirements due to brushless design
- Wide operating temperature range (-20°C to +85°C)
- Compatible with various drive technologies and microstepping options
Technical Specifications
Our stepper motors are engineered to meet rigorous industrial standards. Below is a detailed table of specifications for our flagship models.
| Model |
Step Angle (degrees) |
Holding Torque (Ncm) |
Rated Current (A/Phase) |
Voltage (V) |
Shaft Diameter (mm) |
Weight (g) |
| SM-23B |
1.8 |
45 |
1.5 |
12 |
5 |
250 |
| SM-34C |
0.9 |
120 |
2.8 |
24 |
8 |
550 |
| SM-42D |
1.8 |
200 |
4.0 |
24 |
10 |
850 |
| SM-57E |
0.9 |
350 |
5.6 |
48 |
12 |
1200 |
Applications of Stepper Motors
- Precision positioning in CNC routers and milling machines
- Extruder and bed movement in 3D printers
- Automated conveyor systems and pick-and-place robots
- Medical equipment such as pumps and scanners
- Camera autofocus and lens adjustment mechanisms
- Textile machinery and packaging equipment
Advantages Over Other Motor Types
Stepper motors offer distinct benefits compared to servo motors or DC motors. They provide precise control without encoders, reducing cost and complexity. Their inherent ability to hold position at stop makes them ideal for applications requiring stability. Additionally, stepper motors excel in low-speed scenarios where high torque is necessary, and they are less prone to stalling under load when properly sized.
FAQ: Common Questions About Stepper Motors
What is a stepper motor and how does it work?
A stepper motor operates by converting electrical pulses into discrete mechanical movements. The motor's rotor turns in precise increments, or steps, with each pulse delivered by a drive circuit, allowing accurate control of rotation angle and speed.
What are the main types of stepper motors?
The two primary types are permanent magnet (PM) stepper motors, which offer good torque at low speeds, and hybrid stepper motors, which combine aspects of PM and variable reluctance types for higher precision and torque.
Do stepper motors require feedback encoders?
Typically, stepper motors run open-loop without encoders, as they move in predictable steps. However, encoders can be added for closed-loop control to detect missed steps and improve accuracy in demanding applications.
What is microstepping and why is it used?
Microstepping is a technique that divides each full step into smaller subdivisions, resulting in smoother motion, reduced vibration, and higher resolution positioning. It is commonly used in applications requiring fine control.
How do I choose the right stepper motor for my project?
Consider factors such as required torque, step accuracy, operating voltage, physical size, and environmental conditions. Review our specification table and consult our engineering support for tailored recommendations.
Can stepper motors be used in high-speed applications?
While stepper motors can operate at high speeds, torque tends to decrease as RPM increases. For high-speed requirements, ensure the motor is paired with an appropriate drive and consider inertia matching.
What maintenance do stepper motors need?
Stepper motors are brushless and require minimal maintenance. Periodic checks for dust, debris, and bearing wear are recommended, especially in harsh environments.
Are stepper motors suitable for battery-powered devices?
Yes, but efficiency should be considered. Choosing a model with lower current consumption and using efficient drivers can extend battery life in portable applications.